Engineering
All an SRE needs to know : Automation ERA in Distributed Datastores
Core Contributors : Merwin Joseph Biby, Ritik Singhal & Mannoj Saravanan24 December, 2024
<tl;dr>
– Elasticsearch Upgrade for a cluster takes more than 10hrs by 2SREs manually and entails considerable back and forth.
– SRE has automated the entire flow for rolling upgrades without downtime along with strict guardrails, killswitch, regular slack bots.
– Automation has been executed in prod more than 10 times.
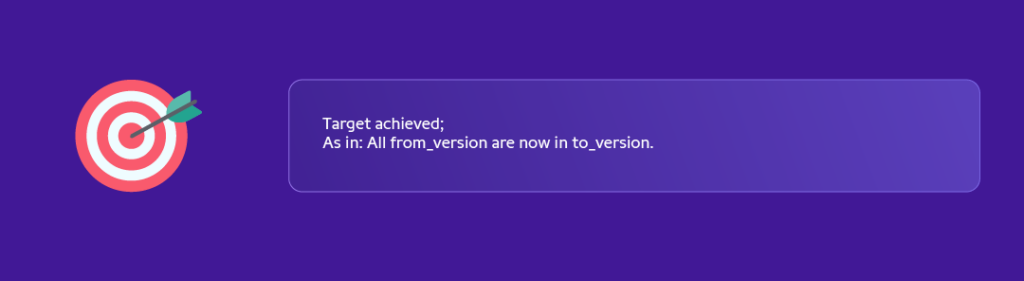
– Now each cluster takes 4 to 6hrs. Also, this can be done parallelly with any no: of clusters, with minimum involvement by an SRE for not more than 30 mins
</tl;dr>
What is Elasticsearch?
- Elasticsearch is a search engine that stores data in Lucene index . Lucene index consists of inverted index. Read this for more info.
- With this inverted index storage, retrieval capability and data management across nodes, that can horizontally / vertically scale up, scale down; provide data availability, user access management, data life cycle management and logging & plotting graphs by making sense out of it; the entire bundle is called ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana). For the Foxtrot use case, however, we use only Elasticsearch or Elasticsearch Cluster.
What is an index?
- The Term
Indexis logically a table in traditional database. - Each index will have 2 properties ; Number of Shards and Number of Replica.
i.e. : { index_name : Student ; Shards: 3 ; Replica : 2 }
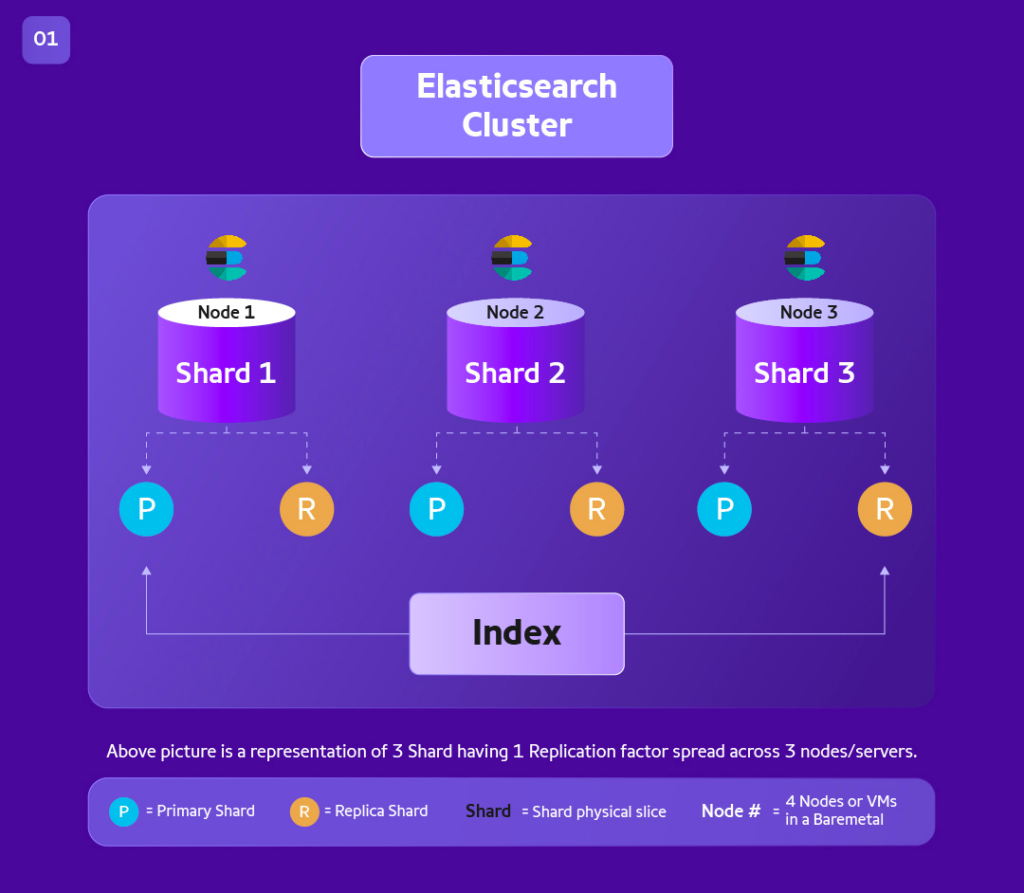
Shard and Replica: There are 3 Servers/Nodes and the student Index will have 3 Shards and each Shard will have its own replica. Shards are nothing but data chunks/slices.
What happens when Node1 goes down?
In case of failure of one node, you will not have data-loss. Because Elasticsearch will not co-host its replica on the same node as primary (Default).
What are called Roles in Elasticsearch?
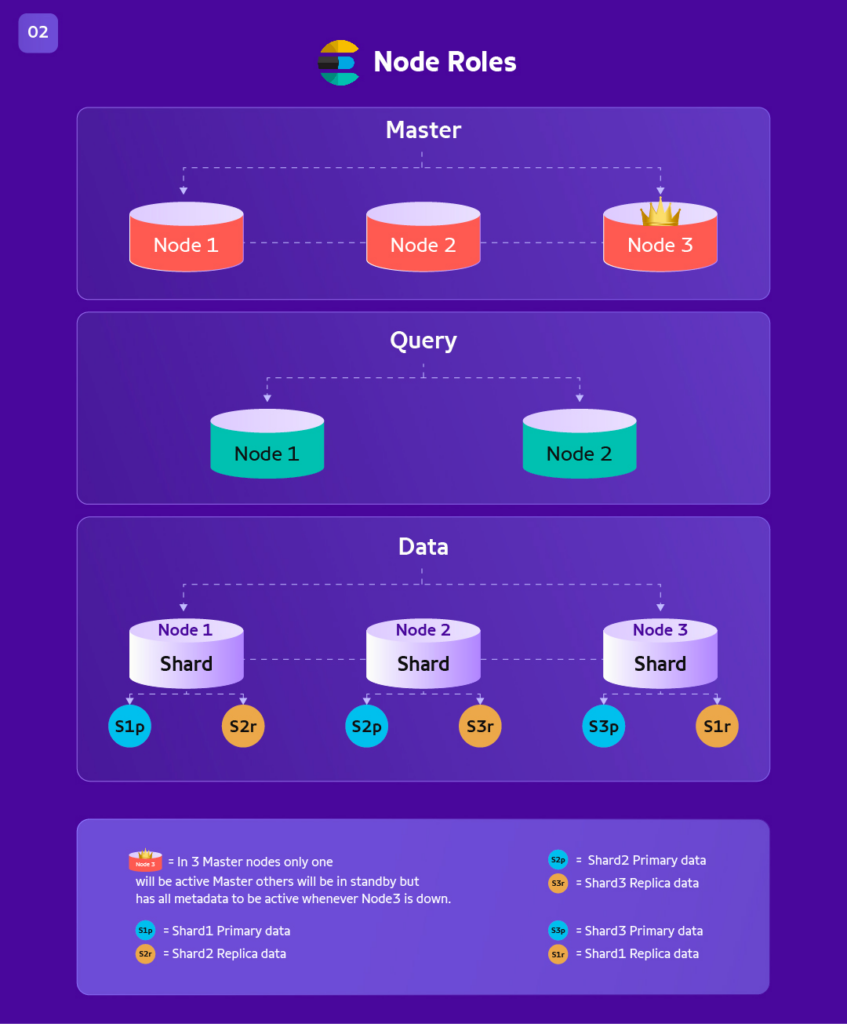
Data: Has data of index, shards, primary/replica as we saw above.
Query: Doesn’t store data, it empowers query/ingestion processing layer for applications to use connection pooling to retrieve or put data.
Master: Maintains the metadata of who has what data/shard and which node. Also takes care of node failure and joining and rebalance operations.
What is Foxtrot and its Infra Foot Print on Elasticsearch?

Elasticsearch Architecture For Foxtrot Application :
BM = Baremetal
Node/VM = Virtual Machine
In 1 BM we have 4 VMs/Nodes
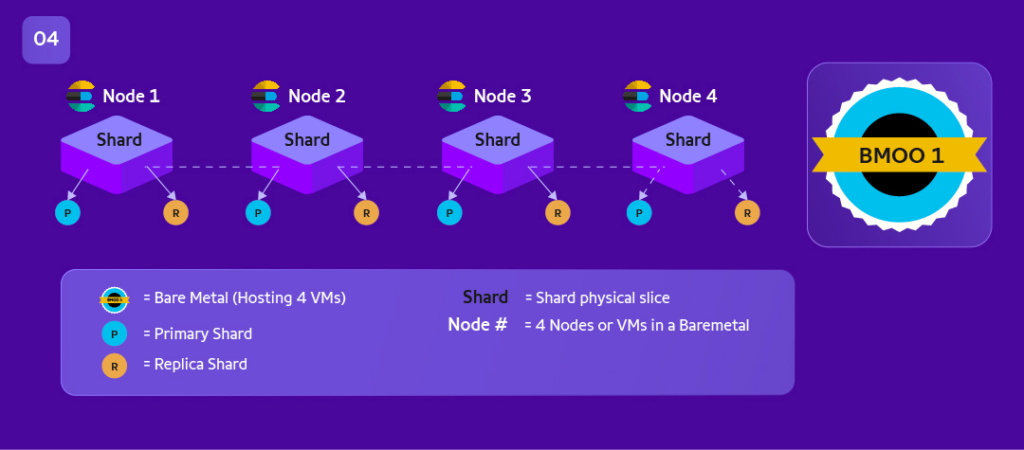
What is a BM Aware?
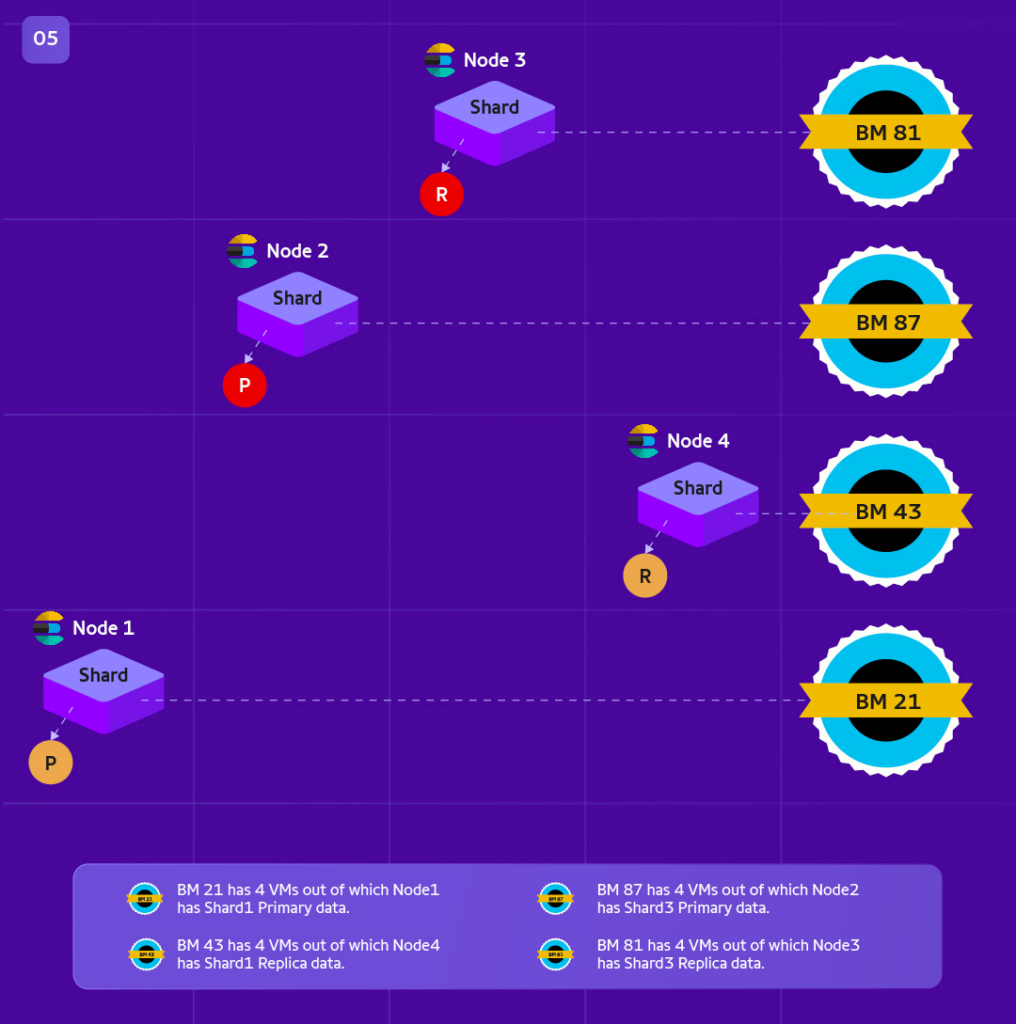
As per above image ,
Data_Yellow ( Primary in BM21.Node1 ; Replica in BM43.Node4)
Data_Red ( Primary in BM87.Node2 ; Replica in BM81.Node3)
Replica data will be spread on a different BM than and not in its Primary’s BM.
Its a cluster level setting , mentioned like below. “allocation” : { “awareness” : { “attributes” : “rack_id” #rack_id is the BM_NUMBER# for us.
Why because chances of BM to go down is higher, and if primary and replica stays in different VMs
Story telling begins:
Let’s get into why the tool exists
Previously, we used Elasticsearch 7.10, and recent perf results for different versions gave us better perf results.
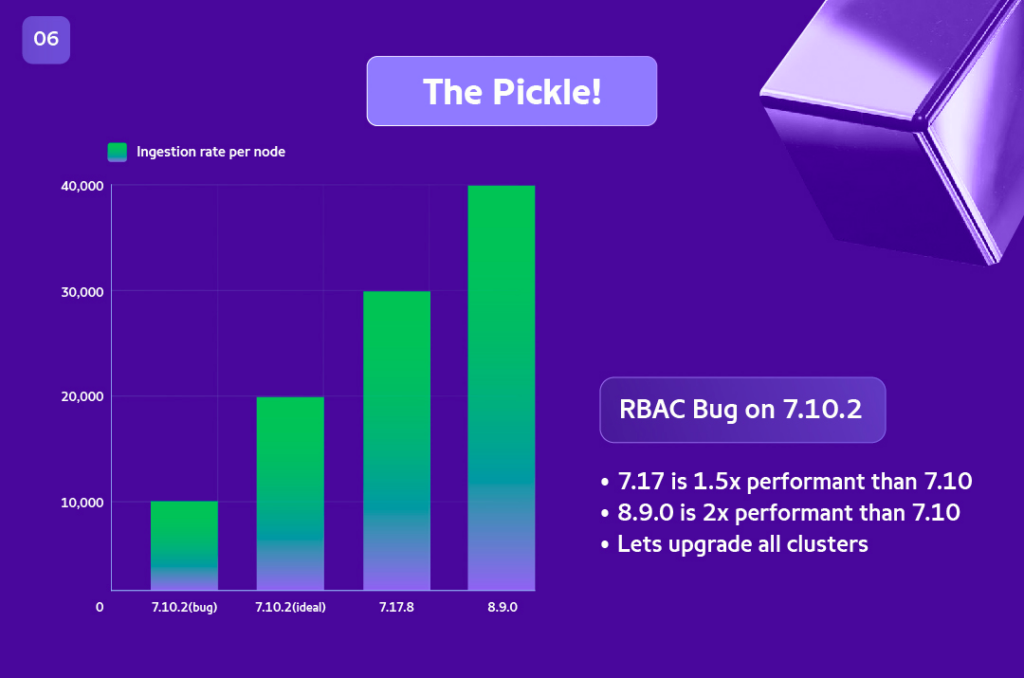
Verdict based on Perf: We had to perform in place upgrade of all clusters from 7.10 to 7.17 and then to 8.9 as there is no direct upgrade to 8.9 from 7.10.

A Look at our Working Architecture :
[The next section is followed by the details]
Outcome is:

Details:


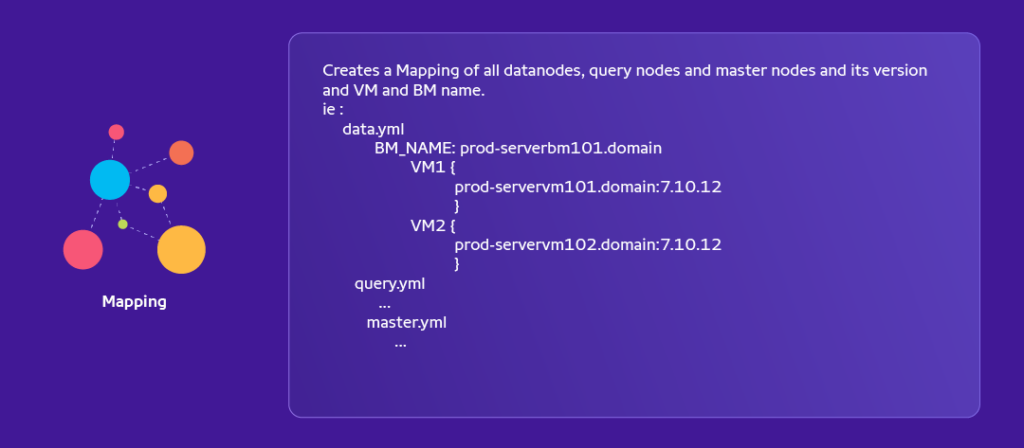








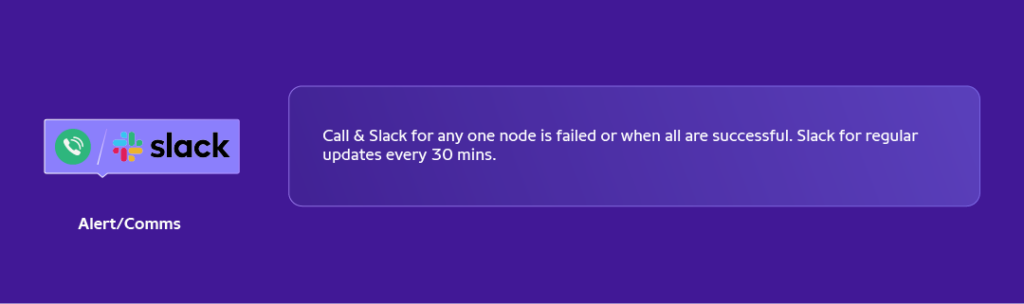
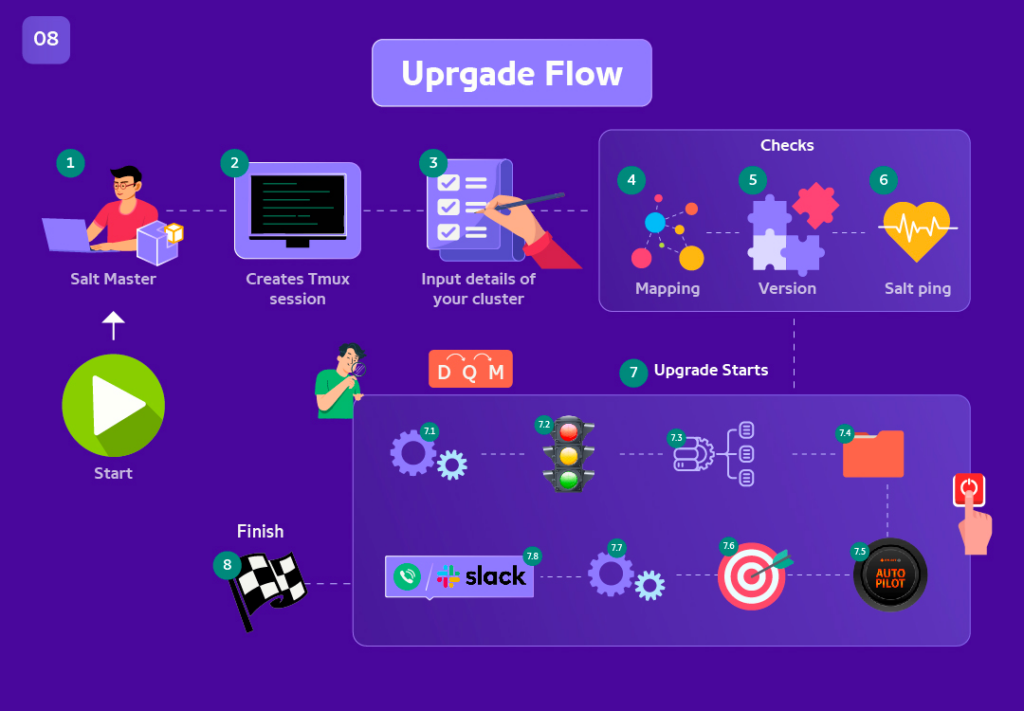
Automation Flow Explanation:
@ UpgradeTime - 2 :
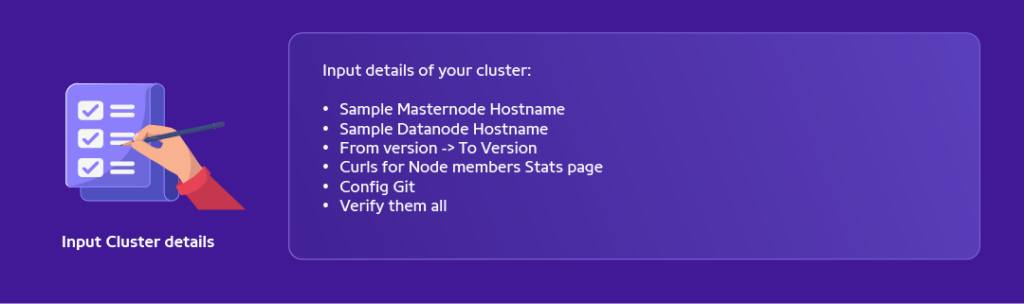
- Input all details for the cluster that one wants to upgrade and verify if it’s all intact and make a note of what the cluster intact signal is going to look like.
@ UpgradeTime - 1 :
- Ping from Salt Master to all its minions/nodes.
- Perform Version checks to all nodes.
- Perform config checks if it’s intact with git config of that cluster.
@ UpgradeTime :
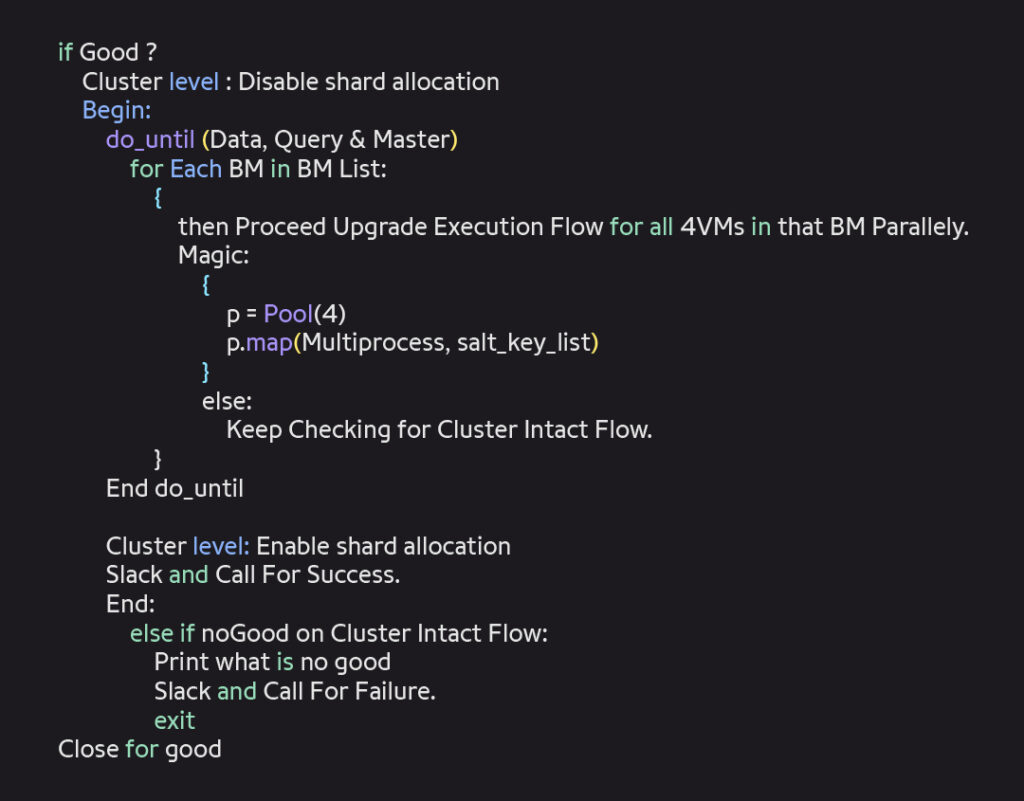
What is Cluster intact Flow ?
- All nodes are in cluster as per data received @
UpgradeTime - 2. - Is Cluster green?
- ( initialize_shards < 10, unassigned_shards = 0)
- active_shards_percent_as_number is 100%
- Are expected Nodes upgraded to Latest Version?
- If all above 5 are good, then give a Green signal.
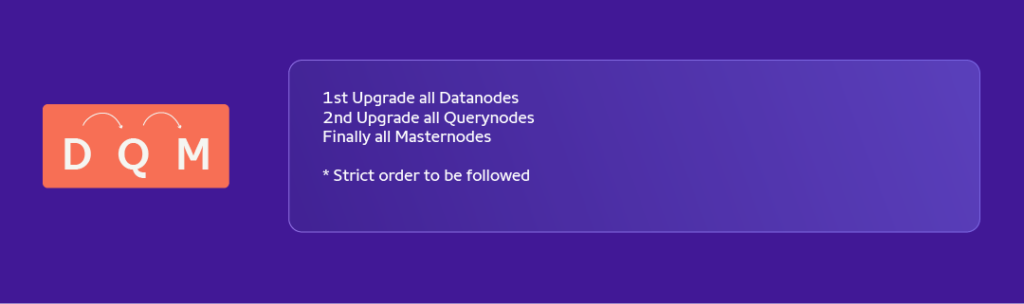
What is Upgrade Execution Flow ?
On Each VM
- Download required package from in-house mirror.
- Backup config files to safe location
- Stop ES
- Upgrade ES
- Start ES
Journey Insights :
- Written in Python.
- It took cumulatively ~35 days to code and contain 3 Phases.
- As of now 11 upgrades have been done successfully in prod with this module.
- Rollback automation was required in stage environment for continuous testing.
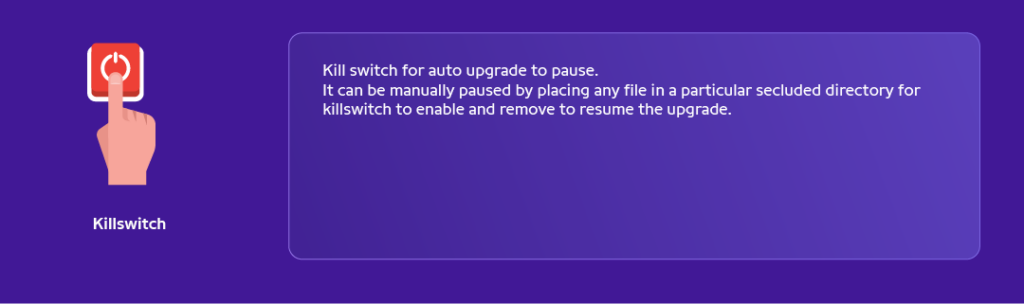
- Guardrails were implemented in such a way that at any time not more than 4VMs are down, which is OK since the cluster is BM aware.
- Success rate of the upgrade is increased in the mapper phase or `@
UpgradeTime - 1`itself. i.e: before actual upgrade kicks off via salt ping checks, version and discrepancy checks. - Adoption to enable ES Upgrader for other team’s ES Clusters in org is possible. (In progress).
- For each test cases/features/tasks, jira has details on why, what and how, so we don’t look back and try to find reasons for the same item again.